Unpacking Anxiety: Understanding Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments
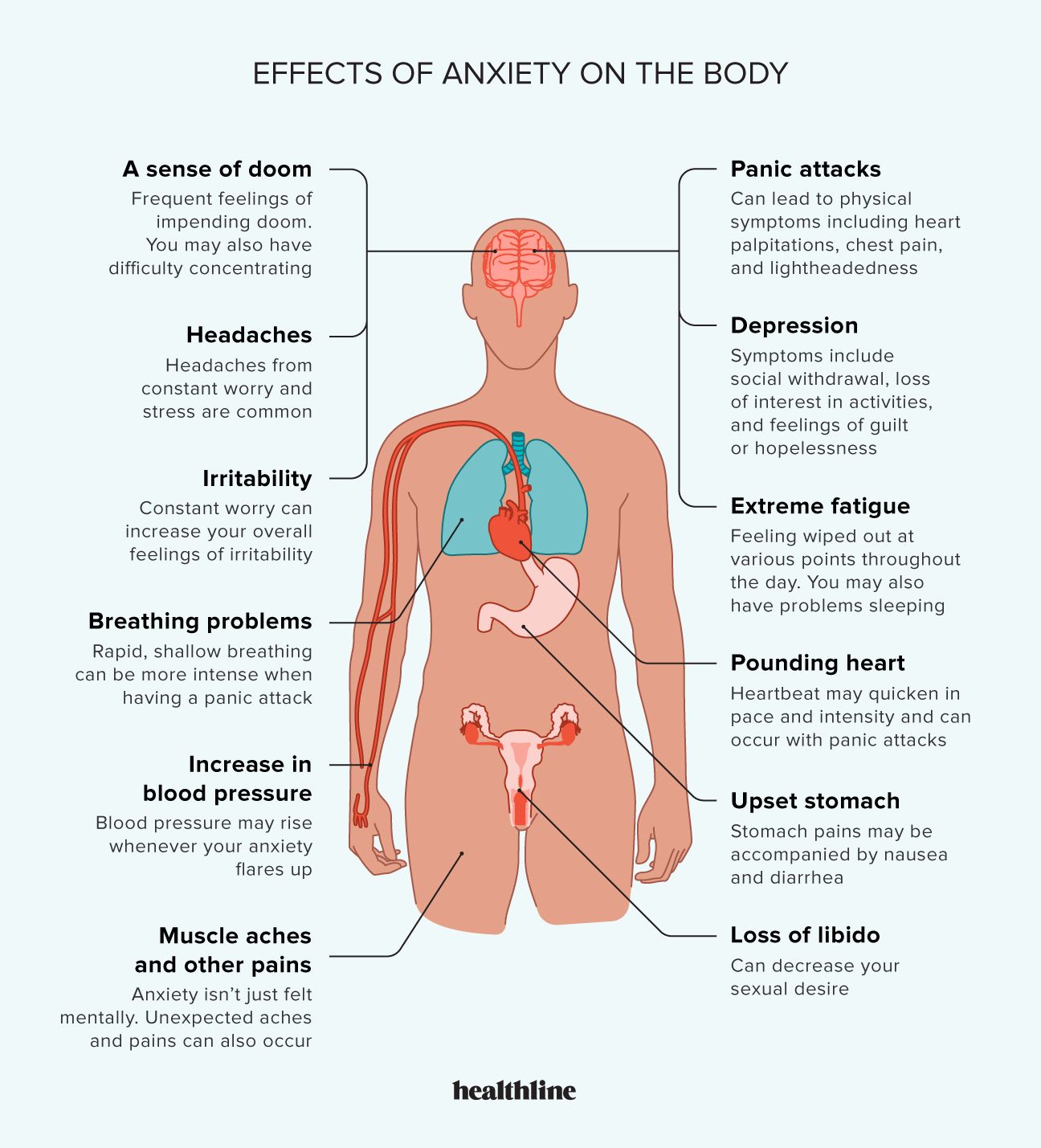
Anxiety is a pervasive mental health issue that affects countless individuals across the globe. While it can manifest as a normal response to stress, persistent and overwhelming anxiety may indicate an underlying disorder. This article aims to clarify the nature of anxiety, outline its symptoms, explore potential causes, and suggest effective treatments to manage this condition.
Defining Anxiety
Anxiety is a reaction to stress that typically serves as a psychological and physiological alert system, warning of potential threats. However, when these responses become excessive and interfere with daily living, they may constitute an anxiety disorder. These conditions can significantly affect a person’s capacity to function and enjoy life to its fullest.
Symptoms of Anxiety
The manifestations of anxiety can vary widely but often include:
Persistent or excessive worry that is difficult to control.
Feelings of nervousness or being tense.
Quick exhaustion, even with minimal activity.
Difficulty in maintaining concentration or experiencing blank spells.
Easily irritated.
Muscle tension and discomfort.
Sleep disturbances and changes, including difficulty falling asleep or restless sleep.
Sudden and intense feelings of fear or panic, known as panic attacks.
These symptoms need to be present consistently for a six-month period for an anxiety disorder to be diagnosed.
Exploring the Causes of Anxiety
The origins of anxiety disorders are typically multifaceted, involving genetic, environmental, and psychological factors:
Genetics: Anxiety can run in families, suggesting that hereditary factors may increase susceptibility to the disorder.
Brain Chemistry: Imbalances in neurotransmitters, the chemicals that transmit signals in the brain, can also contribute to anxiety disorders.
Personality: Individuals with certain personality traits, such as perfectionism or low self-esteem, are more prone to anxiety.
Life Experiences: Traumatic life events such as abuse, a death in the family, or significant life changes can trigger anxiety disorders.
Treatment and Management of Anxiety
Effective treatment for anxiety is available and varies based on the severity of the condition:
Therapy: Psychological therapies like Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) are widely used to treat anxiety. CBT helps individuals understand and alter patterns of thinking that contribute to anxiety.
Medication: Various medications can help control the symptoms of anxiety. These include antidepressants and anxiolytics, which regulate brain chemistry.
Lifestyle Adjustments: Incorporating regular physical exercise, ensuring adequate sleep, maintaining a nutritious diet, and nurturing supportive relationships can help manage anxiety symptoms. Stress management techniques such as mindfulness and meditation are also beneficial.
Conclusion
Anxiety, in its excessive form, can be debilitating, but understanding its symptoms and causes is the first step toward management. With the right combination of treatments, including therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes, those struggling with anxiety can regain control over their emotions and daily life. It’s critical for people feeling overwhelmed by anxiety to seek professional help to develop a tailored approach that addresses their specific needs.
